
A hospital bed mattress, also known as a medical mattress or therapeutic support surface, is a crucial piece of equipment for patient comfort and care. Proper usage is key to maximizing its benefits, from preventing pressure sores to ensuring a good night's sleep. Here's a detailed guide on how to use your hospital bed mattress effectively and safely.
Before you even place the mattress on the bed frame, you need to know what kind you have. There are several common types, and each has a specific use case:
Innerspring Mattress: These are similar to traditional mattresses but are designed to be flexible for use with an adjustable bed frame. They provide basic support and are generally the most affordable option.
Foam Mattress: Offering enhanced pressure redistribution, these are a step up from innerspring models. A pressure redistribution mattress is often made of memory foam or a high-density foam that conforms to the body's shape, reducing pressure points.
Alternating Pressure Mattress (APM): This advanced specialty mattress is ideal for patients at high risk of developing pressure ulcers. It uses a series of inflatable air cells that cycle through inflation and deflation, constantly shifting the pressure points on the body.
Low Air Loss Mattress: This type features a stream of air that escapes through tiny holes in the mattress surface. This helps to keep the patient's skin cool and dry, which is critical for preventing skin breakdown.
Regardless of the type, correct setup is vital.
For a Standard Mattress (Innerspring or Foam):
Place the mattress on the bed frame. Make sure it's centered and aligned properly.
Ensure there are no gaps between the mattress and the side rails that could pose an entrapment risk.
Cover the mattress with a fitted sheet. Note: Using a waterproof mattress cover is highly recommended to protect against spills and incontinence.
For a Powered Mattress (APM or Low Air Loss):
Place the mattress on the bed frame and secure it with any provided straps.
Locate the power unit (the pump). Place it on the footboard of the bed or on the floor, making sure it's not a tripping hazard.
Connect the air hoses from the mattress to the power unit. The connections are usually color-coded or clearly labeled.
Plug the power unit into a wall outlet.
Turn the unit on. It will take some time for the mattress to inflate to the proper pressure. The user manual will provide specific instructions for this process.
For a Powered Medical Mattress:
Pressure Settings: The power unit usually has a dial or digital display for adjusting pressure. Use the patient's weight as a guide. The higher the weight, the higher the pressure setting should be.
Cycle Time: An APM often allows you to adjust the time it takes for the air cells to cycle (e.g., every 5, 10, or 20 minutes). A shorter cycle time provides more frequent pressure relief.
Max Inflate/Static Mode: Many powered mattresses have a "max inflate" or "static" button. This temporarily inflates all the air cells to a firm pressure, which is useful for patient transfers or for when a caregiver needs to perform a task on a stable surface. Remember to switch back to the alternating mode afterward.
For All Mattress Types:
Bed Position: Work with the bed frame's controls to adjust the head and foot of the bed. Elevating the head can aid in breathing and digestion, while raising the feet can help with circulation.
Side Rails: Use the side rails to help the patient reposition themselves and to prevent falls. Always ensure they are locked securely in the up position when needed.
Cleaning: Clean the mattress surface regularly with a mild disinfectant. Always consult the manufacturer's instructions to avoid damaging the material.
Check for Air Leaks: If you're using a powered mattress and notice a drop in pressure, check the air hoses for secure connections and inspect the mattress for any small punctures or tears.
Patient Repositioning: Even with a high-end patient support surface, it is crucial to continue a regular schedule of turning and repositioning the patient. The mattress is a tool to help prevent pressure ulcers, but it does not replace vigilant care.
Monitor Skin: Regularly check the patient's skin for any signs of redness or irritation, especially on bony areas.
By understanding the features of your hospital bed mattress and following these usage guidelines, you can significantly enhance a patient's comfort and health outcomes.
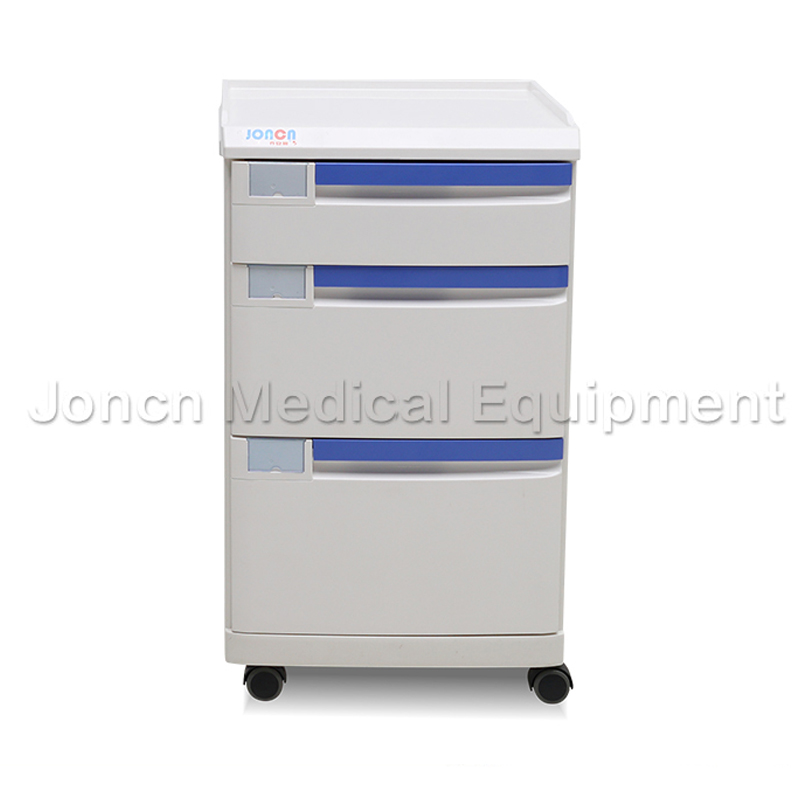

Mixed ABS plastic hospital bedside cabinet with drawer, designed to enhance functionality and efficiency in healthcare settings. Measuring 480*480*810mm, this cabinet features three ABS drawers with h...
See Details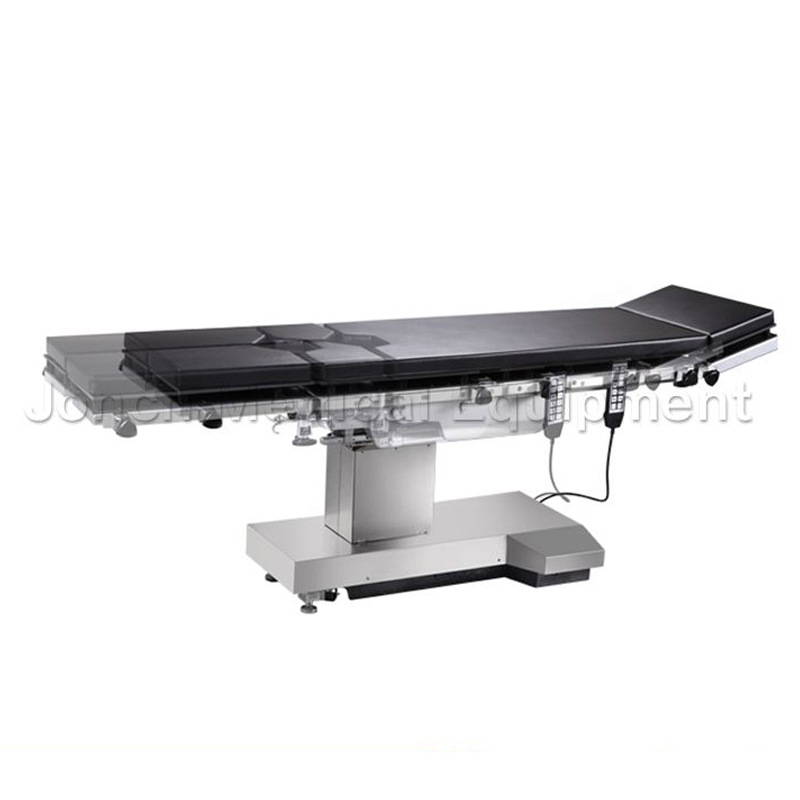
Multi-functional surgical operating table, a solution designed to meet the diverse needs of modern surgical procedures. With precise Technical Parameters including a length and width of 1960mm and 560...
See Details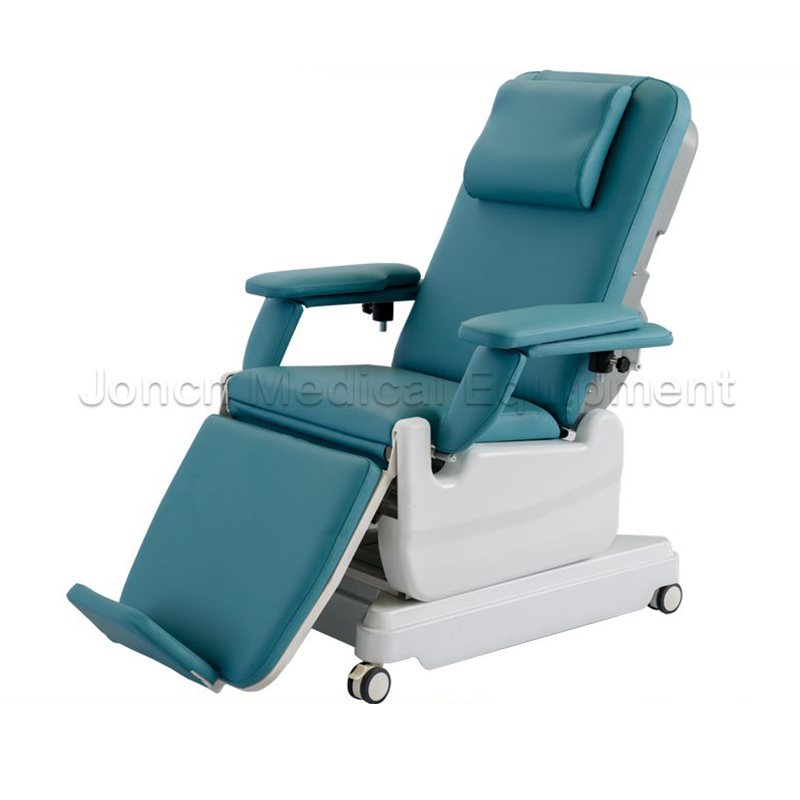
Economic 4 function electric dialysis chair, designed for comfort and functionality in blood supply stations and hospitals. This advanced chair boasts a comprehensive three-section electric design wit...
See Details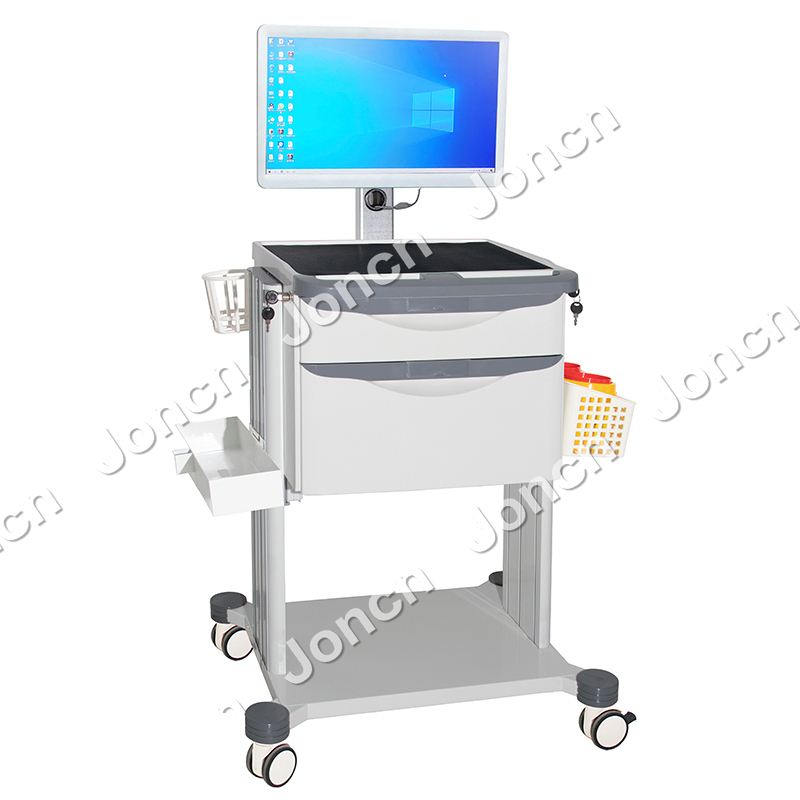
This high-quality wireless nursing trolley, made of easy-clean, eco-friendly, smooth ABS plastic, is quite suitable for the medical working environment.It is designed with the working habits and comfo...
See Details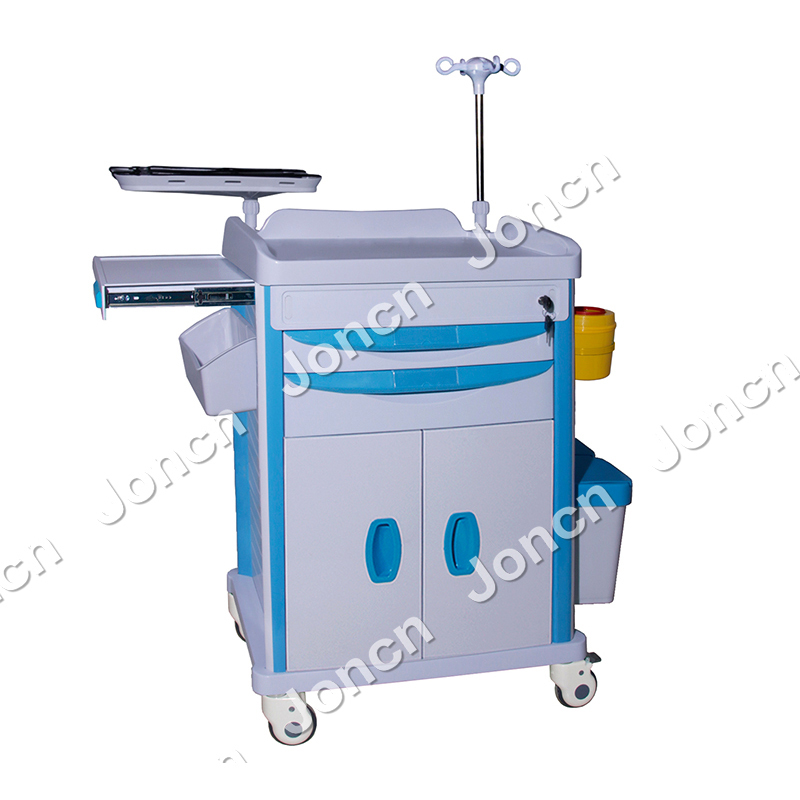
Our emergency medical carts are designed with ergonomics in mind to ensure medical personnel can easily and quickly access and operate the medical supplies on the cart in stressful work environments. ...
See Details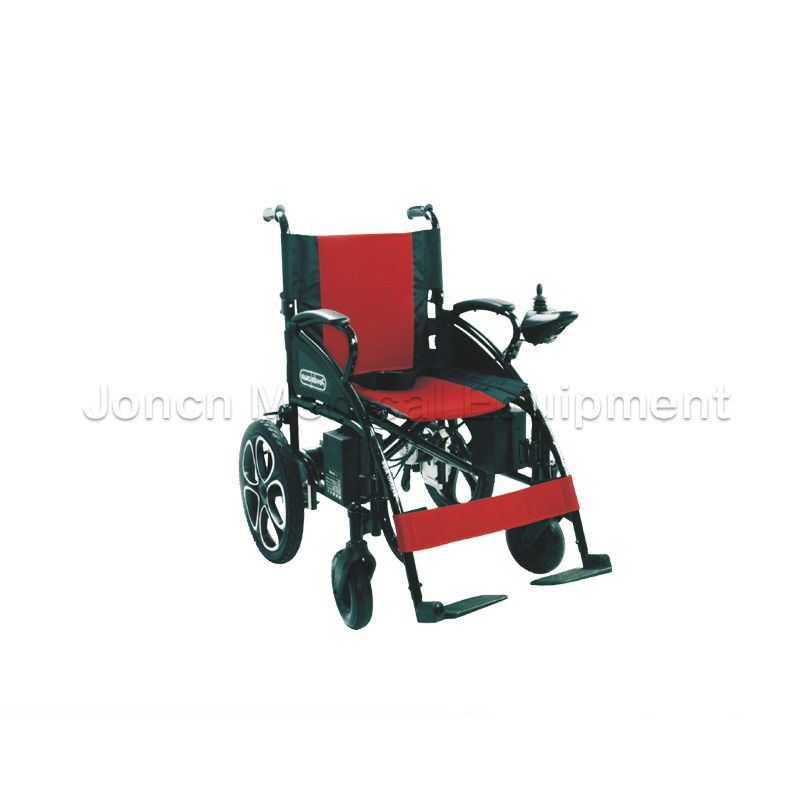
Foldable electric wheelchair with motorized power wheels, specially designed to enhance mobility and comfort for the elderly. Crafted with meticulous attention to detail, this wheelchair boasts a robu...
See DetailsIf you are interested in our products, please consult us
Products
Mobile terminal