
Electric hospital beds are specialized medical beds equipped with electric motors and control systems that allow for effortless adjustment of the bed’s position. These beds are widely used in hospitals, nursing homes, and home care settings to enhance patient comfort, improve clinical outcomes, and assist healthcare providers in delivering care efficiently.
Core Components and Mechanisms
Electric Motors:
At the heart of an electric hospital bed are several electric motors, typically low-voltage DC motors designed for quiet, smooth operation. Each motor is dedicated to adjusting specific sections of the bed — commonly the headrest, footrest, and overall bed height. Some advanced models may have additional motors for lumbar support or Trendelenburg/reverse Trendelenburg positioning (tilting the entire bed).
Bed Frame with Articulating Sections:
The bed frame is segmented into multiple hinged sections. The most common configuration includes:
Backrest section: Allows raising the patient’s upper body.
Seat section: Supports the thighs.
Leg/footrest section: Adjusts the angle or elevation of the legs.
These sections are mechanically linked to the motors via geared drives or linear actuators, which convert the rotary motion of the motors into linear motion to raise or lower each bed segment.
Control Interface:
Electric beds are operated through a wired or wireless control unit. The control interface usually features intuitive buttons or a touchscreen that enable the user (patient or caregiver) to adjust bed positions with precision. Safety features in controls prevent unintended movements, such as child-lock functions.
Power Supply and Backup:
Electric beds are powered by standard AC electrical outlets. To ensure reliability, many hospital beds include an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or battery backup system, allowing adjustments during power outages or emergency situations.
Working Process in Detail
When a button is pressed on the control unit to elevate the head section, an electronic signal is sent to the corresponding motor.
The motor activates, turning a gearbox or a lead screw actuator.
This mechanical action pushes or pulls the linked bed frame section upward or downward smoothly and quietly.
Sensors or limit switches monitor the bed’s position, preventing the motor from overextending and damaging the mechanism.
When the button is released or the desired position is reached, the motor stops immediately.
The bed remains securely locked in the new position due to the self-locking nature of the actuators or gear systems.
Advanced Features in Modern Electric Hospital Beds
Multi-Axial Positioning: Beds can achieve complex positions like Fowler’s position (head elevated 45–60 degrees), Trendelenburg (body tilted feet-up), or reverse Trendelenburg (head-up tilt).
Programmable Presets: Some models allow saving preset positions for quick adjustment, improving workflow efficiency.
Integrated Monitoring Systems: High-end beds may include sensors to monitor patient movement, weight distribution, or vital signs, integrating with hospital IT systems.
Pressure Relief Systems: Beds often support specialized pressure-relieving mattresses or overlays that complement motorized adjustments to prevent pressure ulcers.
Benefits and Clinical Impact
Patient Comfort and Recovery: Electric adjustments allow patients to find optimal positions that ease breathing, improve circulation, reduce swelling, and promote healing.
Reduced Risk of Complications: Proper positioning minimizes risks of pressure sores, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and respiratory issues.
Improved Caregiver Ergonomics: Electric beds reduce the physical strain on nurses and caregivers by minimizing manual lifting or repositioning.
Increased Independence: Patients with limited mobility can independently adjust their bed position, improving dignity and quality of life.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Regular Inspection: Electric motors and control units require periodic inspection to ensure reliable operation.
Battery Maintenance: Backup batteries must be checked and replaced as needed.
Cleaning Protocols: Hospital beds must be cleaned and disinfected following strict infection control standards, including controls and actuators.
Emergency Manual Override: Most electric beds come with manual cranks or emergency release systems to adjust the bed in case of power failure or motor malfunction.
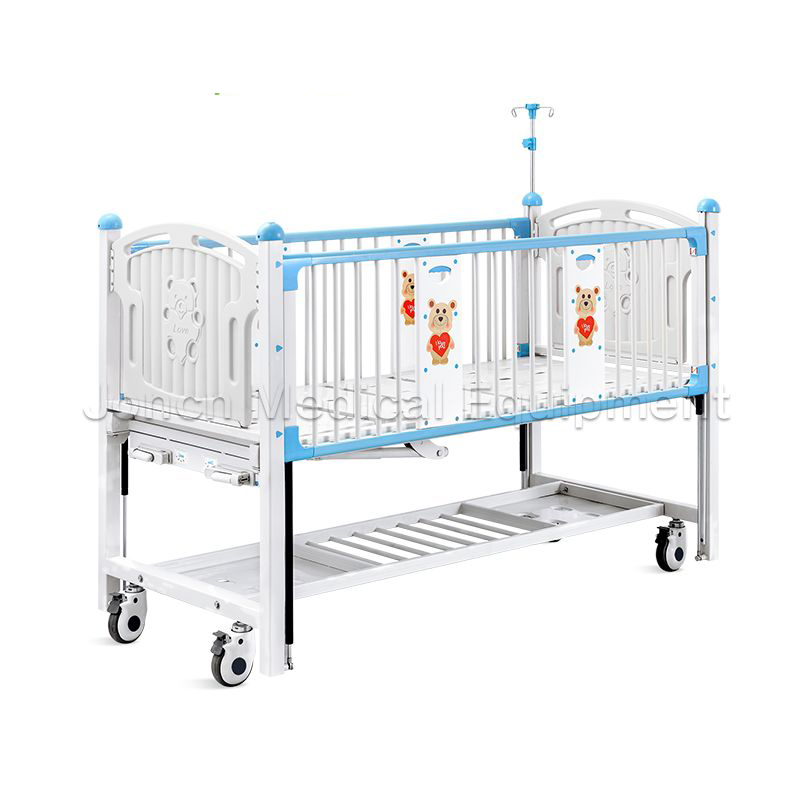
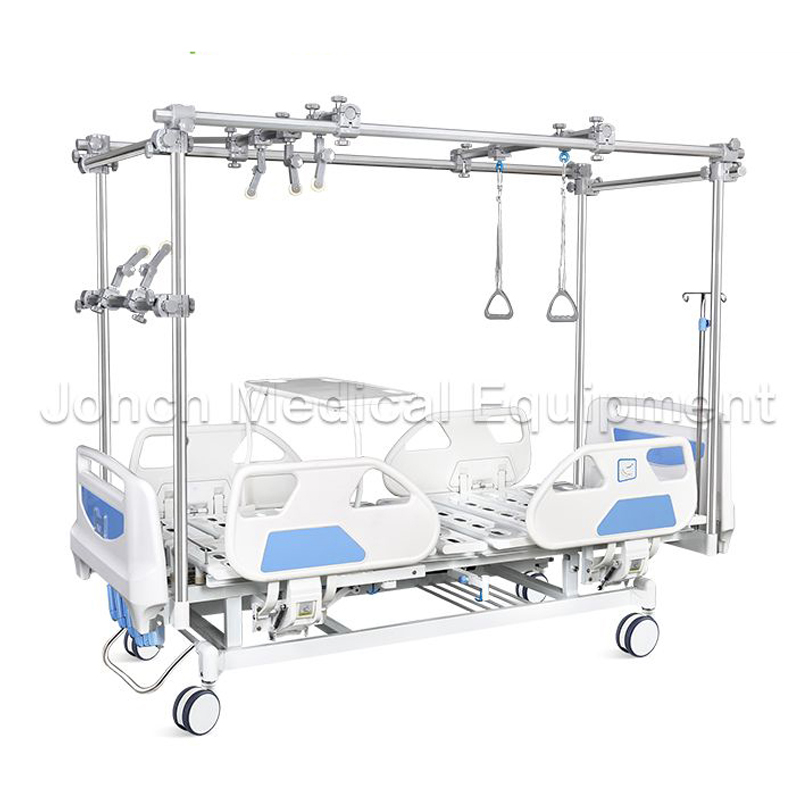


The OD200002 high quality manually adjustable hospital bed. Engineered with precision and versatility in mind, this bed boasts technical parameters that ensure patient comfort and caregiver convenienc...
See Details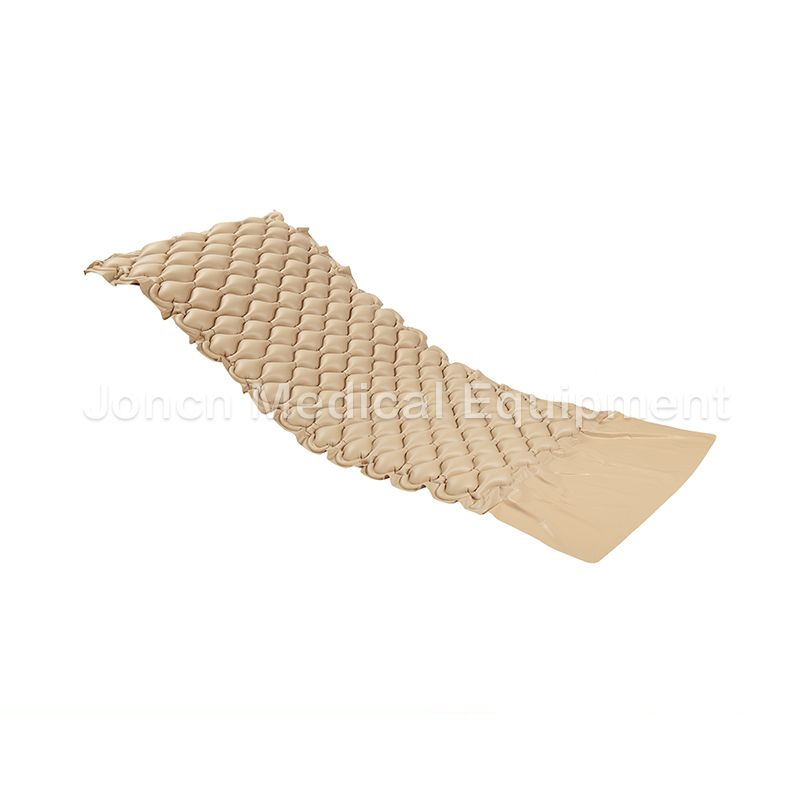
The outdoor camping lightweight portable folding sleeping air mattress is designed for comfort and convenience during your outdoor adventures. This air mattress features a 2.5” Bubble pad arrangement ...
See Details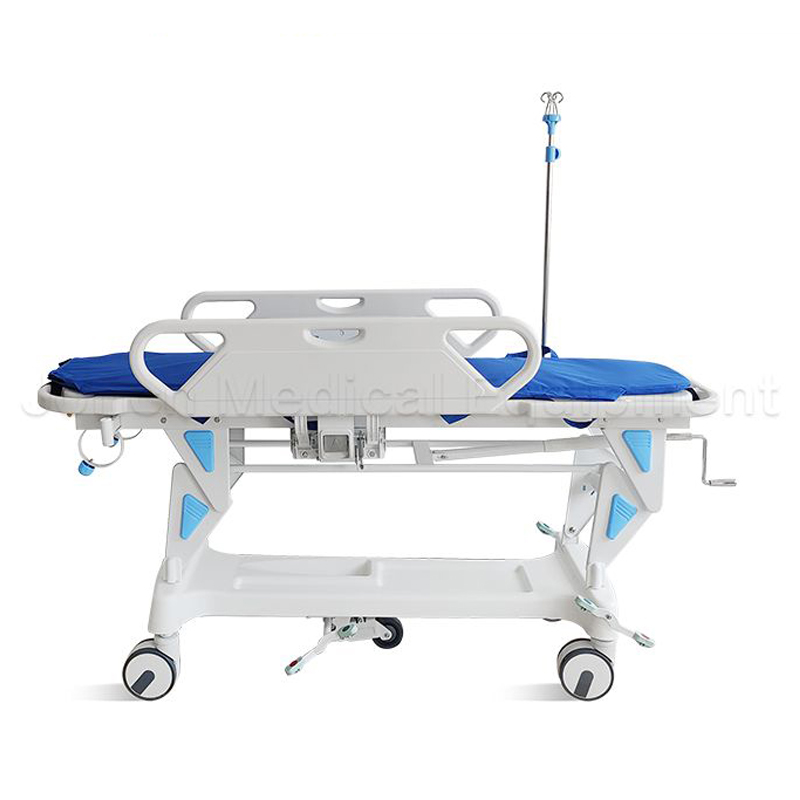
ABS material manual emergency patient transfer trolley, designed for seamless and efficient patient transport within hospital premises. This versatile trolley boasts Technical Parameters of 1900x640x(...
See Details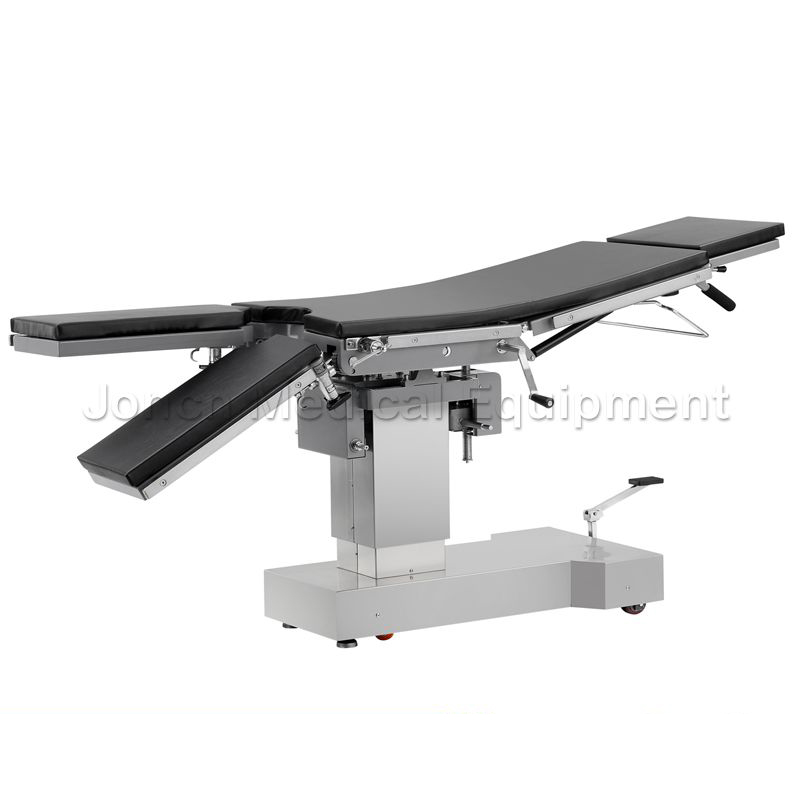
Manual hydraulic surgical table with CE Certification, designed to meet the demanding needs of modern medical procedures with precision and reliability. This advanced surgical table boasts impressive ...
See Details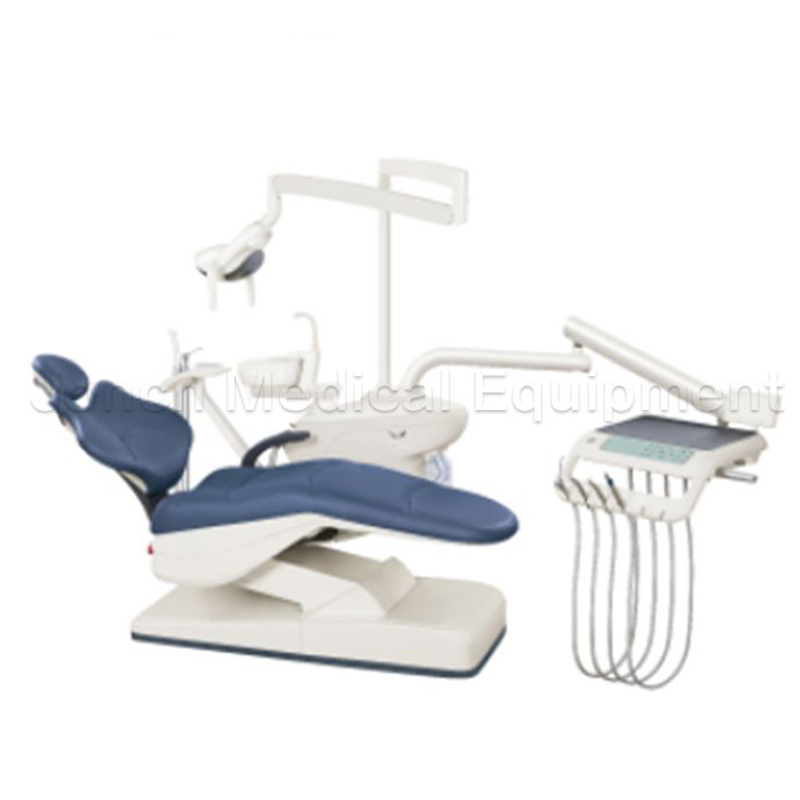
Medical treatment electric dental chair for dentistry departments, designed to elevate patient care and clinical efficiency. This advanced chair operates on both AC 220V/50Hz and 110V 160Hz power sett...
See Details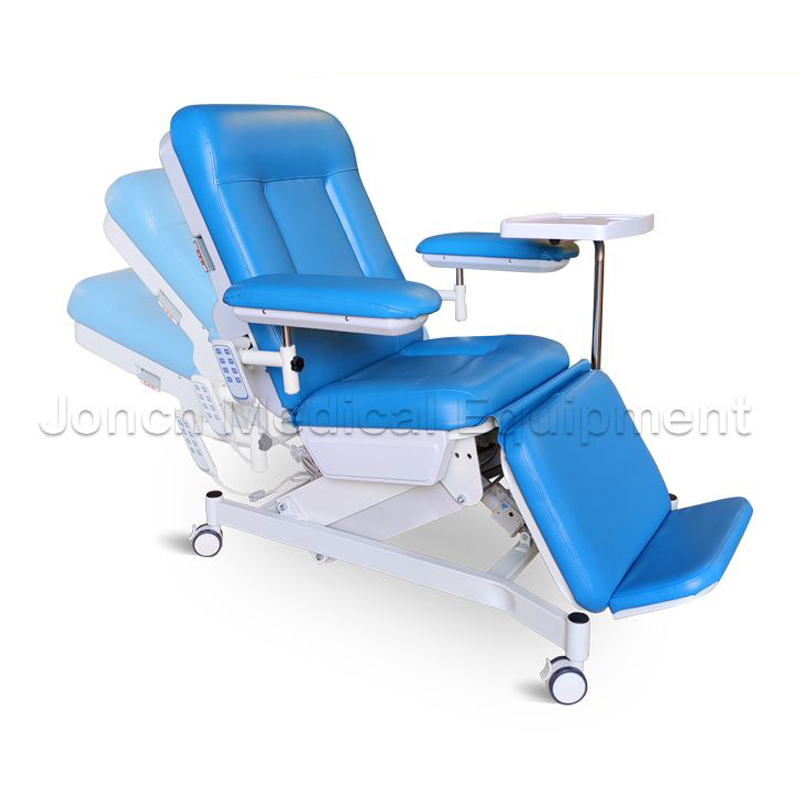
Electric blood transfusion chair for blood collection, an advanced solution designed to elevate patient care and efficiency in medical environments. Engineered with precision and comfort in mind, this...
See DetailsIf you are interested in our products, please consult us
Products
Mobile terminal